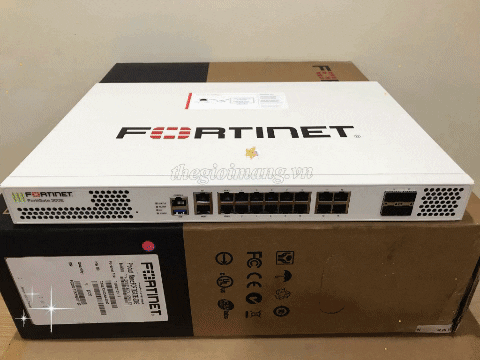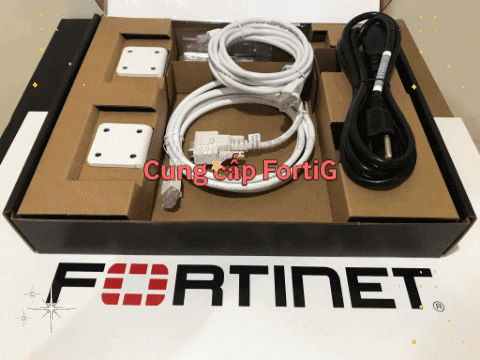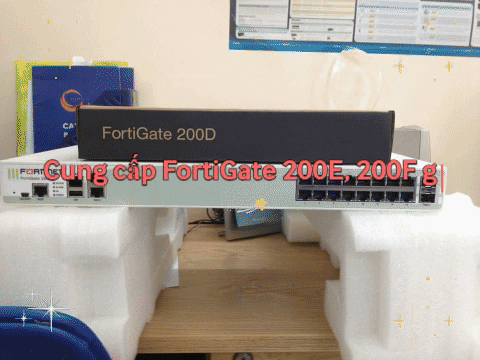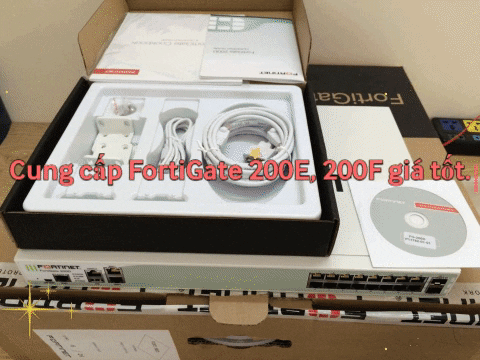
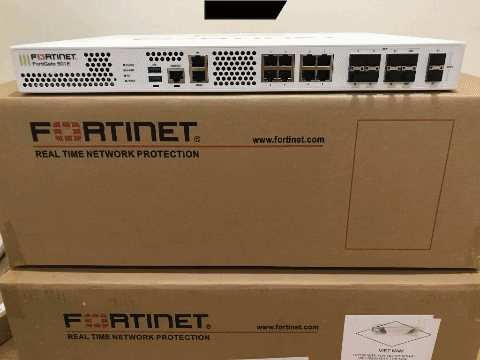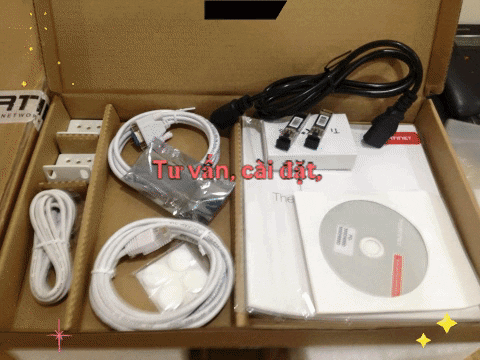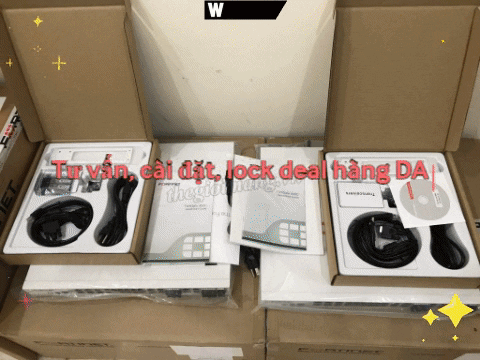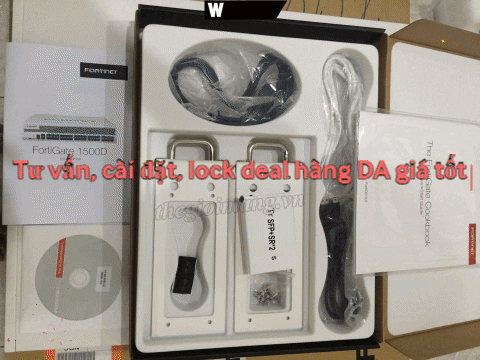

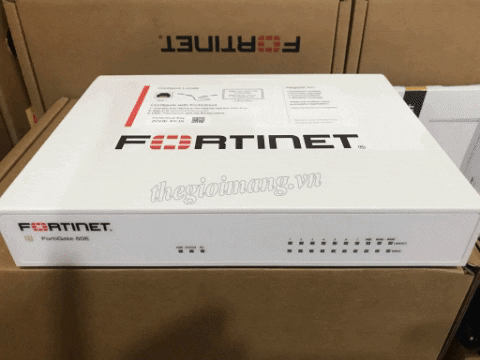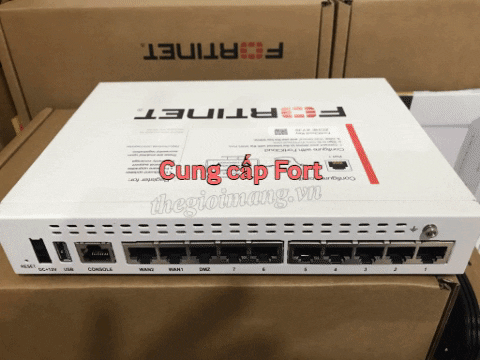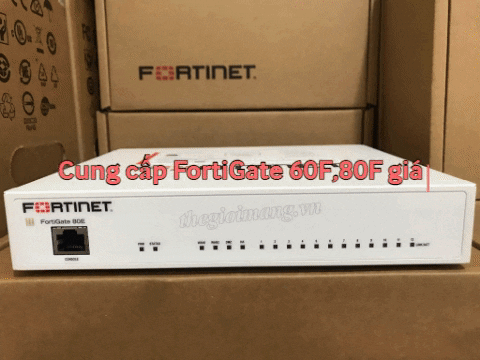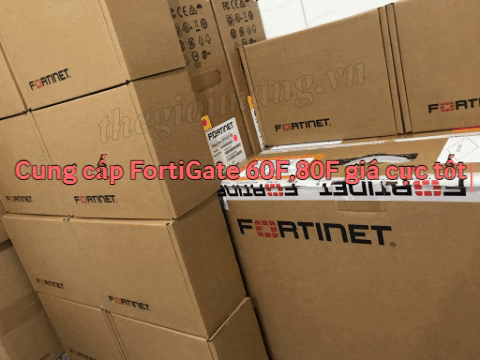

FTTB and FTTC Solution Overview
Thảo luận trong 'Mua bán thiết bị, dịch vụ mạng' bắt đầu bởi dungnhanchi19891, 29/9/20.





Thảo luận trong 'Mua bán thiết bị, dịch vụ mạng' bắt đầu bởi dungnhanchi19891, 29/9/20.